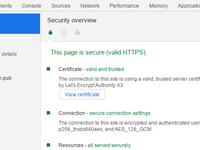
On the modern Internet, most websites already support HTTPS. The SSL/TLS encryption protocol will encrypt users' requests and the website's responses so that malicious users along the way cannot steal or tamper with the information. One important component of SSL/TLS protocol is asymmetric cryptographic algorithms. For these algorithms, the key separates into a public key and a private key , with the public key being public and the private key protected carefully. Accessing an HTTPS website usually follows these procedures: The website sends its public key (as a certificate) to the browser. The browser will verify the public key in case that a man-in-the-middle modified the key in order to block or tap into the communication. The browser (or the operating system)...